| Previous Page |
PCLinuxOS Magazine |
PCLinuxOS |
Article List |
Disclaimer |
Next Page |
ICYMI: NordVPN Data Breach, Only “Dummy” Data Obtained |
|
by Paul Arnote (parnote)
A security investigation by insurance powerhouse Aflac has revealed that more than 22 million affiliated people were affected by a data breach in 2025, according to an article from TechRepublic. The breach, which, according to Aflac, has been contained, involved customers’ personally identifiable information (PII). According to the insurance company, some suspicious activities were observed in June 2025. The abnormal network activity was traced to an advanced cybercrime group, warranting a full-scale investigation. Aflac did not publicly identify a specific name, which may be revealed in the future as more information is revealed. There are warning signs that your home network may have been compromised, such as unusual traffic patterns and slowdowns in system performance, but now there's a simple tool to help determine if your router or connected devices are being used to conduct malicious activity, according to an article from Lifehacker. IP Check, from threat monitoring firm GreyNoise, will alert you if your IP address has been observed scanning the internet as part of a botnet or residential proxy network. As GreyNoise outlines, residential IP compromise often isn't obvious to the user because you're still able to conduct business as usual, such as streaming, emailing, and web browsing. All the while, though, threat actors are routing malicious activity through your home IP address and can potentially exploit your network for everything from account takeovers to malware distribution. Humanoid robots are moving past simple metal and gears to something much more sensitive. In a major leap for embodied intelligence, researchers in China have developed a “neuromorphic” electronic skin (NRE-skin) that allows robots to experience touch, detect injury, and even react to pain through reflexive movements, mimicking the way the human nervous system protects the body, according to an article from eWeek. While most current robotic skins are limited to basic pressure sensing using complex, bulky wiring, this new NRE-skin takes a page out of biology. Human skin is a sophisticated network where nerve endings turn touch into “pulses” for the brain to read. The NRE-skin does the same, converting physical pressure into neural-like pulse trains. According to the research team, this hierarchical design allows the robot to understand not just that it’s being touched, but exactly where and how hard. As Ars Technica reports, this system uses these activity spikes to create “something akin to a bar code that helps identify which sensor the reading came from.”  NordVPN denied allegations that its internal Salesforce development servers were breached, saying that cybercriminals obtained “dummy data” from a trial account on a third-party automated testing platform, according to an article from Bleeping Computer. The company's statement comes after a threat actor (using the 1011 handle) claimed on a hacking forum over the weekend that they stole more than 10 databases containing sensitive information like Salesforce API keys and Jira tokens, following a brute-force attack against a NordVPN development server. “Today I am leaking +10 DB's source codes from a NordVPN development server. This information was acquired by bruteforcing a misconfigured server of NordVPN, which has salesforce and jira information stored. Compromissed information: SalesForce api keys, jira tokens and more,” the threat actor said. However, as NordVPN revealed today, this is actually test data stolen from a temporary test environment deployed months earlier during trial testing a potential vendor for automated testing. The Lithuanian VPN service added that the test environment had no connection with its own infrastructure and that the stolen data doesn't include sensitive customer or business information. Hackers no longer need to break into WhatsApp accounts. They just let themselves in. Cybersecurity researchers at technology firm Gen Digital have uncovered a new attack that quietly links an attacker’s browser to a victim’s WhatsApp account, giving them ongoing access without raising alarms, according to an article from TechRepublic. The technique, known as “GhostPairing,” exploits WhatsApp’s device-linking feature, which allows users to connect multiple devices to a single account. By abusing this legitimate function through social engineering, attackers can remain invisible while monitoring messages and gathering personal information. Researchers warn that critical flaws in popular Bluetooth headphones could enable eavesdropping, data theft, and smartphone compromise, according to an article from eSecurity Planet. The vulnerabilities impact devices from major brands, many of which have yet to be patched. The flaws “… might allow eavesdropping via the device’s microphone,” said researchers. The vulnerabilities impact Bluetooth headphones and earbuds powered by Airoha system-on-chips (SoCs), which are widely used across the consumer electronics market. The flaws are tracked as CVE-2025-20700, CVE-2025-20701, and CVE-2025-20702, with CVSS scores ranging from 8.8 to 9.6, indicating high to critical severity. Despite initial disclosure to vendors in June 2025, some manufacturers have yet to fully patch affected products at the time of publication.  Image by schoithramani from Pixabay OX Security researchers found that more than 900,000 Chrome users unknowingly exposed sensitive AI conversations after installing malicious browser extensions masquerading as legitimate productivity tools, according to an article from TechRepublic. The campaign highlights how trusted browser ecosystems can be quietly abused to siphon off proprietary data, personal information, and corporate intelligence at scale. The malware “… adds malicious capabilities by requesting consent for ‘anonymous, non-identifiable analytics data’ while actually exfiltrating complete conversation content from ChatGPT and DeepSeek sessions,” OX researchers said in a blog post. Once installed, the malicious Chrome extensions established persistent visibility into users’ browsing activity by leveraging the chrome.tabs.onUpdated API, which allows extensions to monitor tab changes and page loads in real time. This capability enabled the malware to silently observe when users navigated to AI platforms such as ChatGPT or DeepSeek without raising suspicion. U.S. officials are investigating a suspected Chinese cyber espionage operation compromising email systems used by congressional staff working on House national security committees, according to an article from Bank Info Security. The activity, detected in December, appears to have originated from the threat actor commonly tracked as Salt Typhoon, according to researchers tracking the operation. It appears to have affected staff supporting committees with oversight of China policy, foreign affairs, intelligence and the military. There is currently no public indication that lawmakers' own accounts were accessed, but the targeting of staff networks is raising new concerns about how foreign adversaries may have extracted strategic insights from systems handling sensitive data. Scientists have created a highly efficient method to produce tagatose, a rare sugar that tastes like real sugar but has fewer calories and a much smaller impact on blood sugar, according to an article from ScienceDaily. Made using engineered bacteria, it could offer a healthier, more natural-feeling alternative to today’s sugar substitutes. Tagatose exists naturally, but only in very small quantities compared with common sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. It appears in milk and other dairy products when lactose breaks down under heat or enzymatic activity, including during the production of yogurt, cheese, and kefir. Tiny amounts of tagatose are also present in fruits like apples, pineapples, and oranges. However, it typically makes up less than 0.2% of the sugars found in these natural sources. Because of this scarcity, tagatose is usually produced through manufacturing rather than extracted directly from foods. 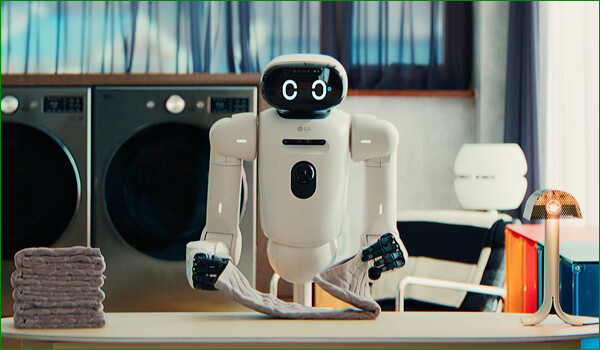 LG Electronics LG Electronics showcased LG CLOiD™, an AI-powered home robot at CES 2026, representing its “Zero Labor Home” vision where intelligent machines handle everyday chores through robotics and connected home integration, according to an announcement on the electronics company’s website. LG CLOiD is a robot that uses AI and vision-based technology to perform household tasks like cooking and laundry, connecting seamlessly with LG’s ThinQ ecosystem to automate home life. By unveiling LG CLOiD and its new actuator technology, LG takes a major step toward AI-driven homes, combining robotics, smart appliances and Physical AI to make housework effortless and time-saving. In 2024, scientists stumbled upon a potential new treatment for hereditary-patterned baldness, the most common cause of hair loss in both men and women worldwide, according to an article from ScienceAlert. It began with research on a naturally occurring sugar that helps form DNA: the 'deoxyribose' part of deoxyribonucleic acid. While studying how these sugars aid wound healing in mice when applied topically, scientists at the University of Sheffield and COMSATS University in Pakistan noticed that the fur around treated lesions grew back faster than in untreated mice. Comcast is set to appear in court in mid-January as software development company Promptu Systems pushes forward with a revived patent infringement lawsuit originally filed back in 2016 and brought back in 2024, according to an article from Cord Cutter News. The case, which centers on allegations of unauthorized use of voice recognition and command technologies, has been given new life following a recent appellate ruling that overturned key aspects of the initial dismissal. The proceedings are scheduled to commence in a Pennsylvania district court on Thursday, January 15, 2026, where Promptu aims to present fresh arguments demonstrating how Comcast incorporated its patented innovations into various consumer devices. This revival stems from a decision last week by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, which determined that the lower court had mishandled the interpretation of critical patent terms. As a result, Promptu now has the opportunity to reargue its claims, potentially exposing Comcast to substantial legal and financial repercussions if the infringement is upheld.  Image by Ernesto Barrachina from Pixabay The YouTuber named LabCoatz has shaken the soda world with claims that he cracked the code on the flavor of original Coca-Cola, according to an article from The Takeout. Using a mass spectrometer and a whole lot of science, LabCoatz — real name Zach Armstrong — and two other YouTubers mapped out the recipe of the iconic soda by recording the chemical signature of each flavor. Then, they replicated those flavors in a laboratory-made drink that testers said tastes like the real thing. People are living longer these days, with the average life expectancy for people in the U.S. reaching 80.7 years for women and 74.1 for men, according to a scientific study published in JAMA, according to an article from the Huffington Post. Unfortunately, for many people, their later years are not spent in good health. According to the same study, the U.S. has the largest gap between healthspan (the number of years one spends in good health) and lifespan (the number of years one lives). Dementia is one of the biggest threats to healthspan. According to the National Institutes of Health, researchers estimate that 42% of Americans over 55 will eventually develop dementia. Ready for some good news? You can control your brain health more than you probably think. A 2024 report published in The Lancet says that an estimated 45% of dementia cases are preventable through diet and lifestyle habits. Certainly, it’s our everyday habits that impact our health the most, including our brain health. There’s one common habit in particular that brain health experts we talked to said could be increasing one’s dementia risk without them even realizing it. Despite all of the horror stories about Google, it does still remain one of the most popular sites in the world for search, email, and many other services offered by them. If you still use Gmail as your primary email (I’m guilty), Lifehacker has an article about some Gmail “hacks” that will make your life easier … well, at least make managing your Gmail account a lot easier. 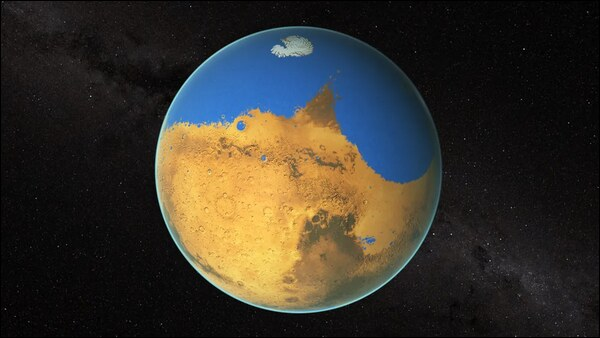 NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Evidence of free-flowing water in Mars’s past has been mounting for a long time. River deltas, water-altered minerals, and more have painted a picture of a wet world long ago. What remains a mystery is its climate. Was it cold and wet or mild and wet? Lots of ice or a stable ocean? New evidence suggests that about 3 billion years ago, there was a hemisphere-spanning ocean in the north of Mars, according to an article from IFL Science. This comes from a team studying Valles Marineris, the largest − though not the longest − canyon system in the Solar System. It is more than 4,000 kilometers (2,500 miles) long and 200 kilometers (120 miles) wide. If you’re a billionaire looking to jump into philanthropy there are hundreds of different causes to support. Fans of the seemingly always-cash-strapped NASA will certainly be cheering after news that a former Google CEO is going to foot the bill for a modern, updated replacement to the Hubble Space Telescope, according to an article from the Good News Network. The 3-decade-old observatory which gave so many individuals among the Millennial and Generation X demographics their first views of the cosmos is still operational, but struggles over funding priorities and a new focus on physical exploration rather than photographic exploration will undoubtedly see it retired in the coming years. Eric Schmidt, CEO of Google from 2001 to 2011, and the company’s executive chairman from 2011 to 2015, has announced together with his wife Wendy that their estate will philanthropically fund 4 telescopic observatories, one of which, called Lazuli, will be launched into space and bring capabilities that would outclass Hubble. NASA, along with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), announced Tuesday a renewed commitment to their longstanding partnership to support the research and development of a fission surface power system for use on the Moon under the Artemis campaign and future NASA missions to Mars, according to an article from the NASA website. A recently signed memorandum of understanding between the agencies solidifies this collaboration and advances President Trump’s vision of American space superiority by deploying nuclear reactors on the Moon and in orbit, including the development of a lunar surface reactor by 2030. This effort ensures the United States leads the world in space exploration and commerce.  Image by Clker-Free-Vector-Images from Pixabay Many people who are prescribed statins to lower cholesterol end up stopping the medication because of muscle pain, weakness, or ongoing fatigue, according to an article from Science Daily. These symptoms are among the most common reasons patients abandon the drugs. New research from Columbia University suggests a possible explanation for why this happens in some individuals. The study indicates that certain statins can attach to a protein inside muscle cells, triggering a leak of calcium ions that disrupts normal muscle function. More than 9 out of 10 Alzheimer's cases could be driven by specific variations in a single gene and the protein it produces, a new study reveals, suggesting that treatments targeting this well-known gene could prevent the disease from developing in the majority of instances, according to an article from ScienceAlert. The gene in question, APOE, has long been associated with Alzheimer's risk. What's new here is the way the different variations of the gene have been analysed and mapped against the chances of developing Alzheimer's. It turns out that the APOE combination we're born with could be even more important than previously realized. Researchers led by a team from University College London (UCL) took a fresh look at the three main variations of the APOE gene: ε2 (linked to a protective effect against cognitive decline), ε3 (historically considered the normal or neutral version), and ε4 (already known to significantly increase Alzheimer's risk). They found, based on four genetic datasets covering almost 470,000 people, that ε3 isn't actually neutral – it can be considered a major risk factor. Part of the reason this hasn't been flagged before is that it's the most common variant of APOE, found in around three-quarters of the population. Amazon wants Walmart’s shoppers … and it’s willing to build a small city to get them. The company has plans to roll out a sprawling new brick-and-mortar experiment aimed squarely at Walmart’s long-standing dominance in physical retail, according to an article from TechRepublic. The new 229,000-square-foot facility, proposed for the Chicago suburbs (specifically, Orland Park), marks Amazon’s latest attempt to build a grand-scale physical presence. According to GeekWire, experts call the initiative a clear sign of “Walmart jealousy,” as the company plans to leverage its digital tools, such as in-store app ordering, to disrupt its biggest rival. The end goal? To challenge Walmart’s multibillion-dollar hold on consumer dollars.  Scammers are flooding LinkedIn posts with fake “reply” comments that appear to come from the platform itself, warning users of bogus policy violations and urging them to visit an external link, according to an article from BleepingComputer. The messages convincingly impersonate LinkedIn branding and in some cases even use the company’s official lnkd.in URL shortener, making the phishing links harder to distinguish from legitimate ones. Over the past few days, LinkedIn users have been targeted with bot-like activity from several LinkedIn-themed profiles commenting on their posts. These posts falsely claim that the user has “engaged in activities that are not in compliance” with the platform and that their account has been “temporarily restricted” until they visit the specified link in the comment. If you don't like how the internet makes you feel right now, you're not alone. The entire ecosystem seemingly exists to manipulate you, which can make finding clarity hard. An important step is recognizing when you're being manipulated. RageCheck is a potentially useful tool here, according to an article from Lifehacker. Built using concepts from social science research, this website can analyze any link or screenshot. It points out examples of potentially manipulative language, from us-versus-them framing to emotionally loaded phrasing. “The system analyzes text for linguistic patterns commonly associated with manipulative framing—language optimized to provoke high-arousal reactions over understanding,” says the methodology page. “It does not assess factual accuracy or political bias.” Using the site is simple: just paste a link to an article and hit Enter. After a few moments, you'll see a statistical breakdown of the potentially manipulative language in the piece across five categories—emotional heat, us versus them, moral outrage, black-and-white thinking, and fight picking. The article is excerpted below, with examples of these tactics highlighted. In the left panel you'll see a “Bait Score,” which is an attempt to calculate how manipulative the article is being. Below that, you'll see a list of the potentially manipulative techniques employed in the article. None of this is intended to be used as an alternative to fact-checking or serve as some kind of truth-detecting machine. “A high score means content uses manipulative framing—it doesn't mean the underlying claims are false,” says the about page. “Conversely, a low score doesn't mean content is true.” Have you ever wondered if the image you’re looking at is an AI-generated “fake?” Well, that’s exactly what one article from eWeek intends to help you out with: tips on how to spot AI Generated Images. A couple of years ago, spotting an AI-generated image was almost a game. You didn’t need sharp eyes; just count the fingers, or recall that bizarre AI clip of Will Smith eating spaghetti. The results were fascinating, funny… and very obviously fake. Today, that’s no longer the case. AI image generators have gotten dramatically better, turning out photos that can look realistic enough to pass at a quick glance… and sometimes even longer. The good news: AI still isn’t perfect. Well, not yet. Even the best-generated images tend to stumble over certain details, especially when scenes get busy or realistic in small, human ways. If you know where to look, those slip-ups are surprisingly easy to spot.  Picture this: you created your Gmail account WAY back, over 20 years ago. Today, it remains your go-to email account. However, back when you set up your Gmail account, you thought it would be cool to showcase your passion with an email address, something like OptimusPrimeRules@gmail.com or ben_and_julie_4ever@gmail.com (and you can barely even remember what attracted you to Julie in the first place). As is typical of younger people, there’s not much thought that goes into how that might sound when fielding job offers (or any other professional endeavor). It’s about as far away from a “professional” sounding email as you can get. And, with Gmail, you’re pretty much stuck with that email address, unless you set up another email account. Or at least, that used to be the case. Google has recently started rolling out the ability to change your Gmail email address, with some limitations, according to an article from Lifehacker. A new study led by researchers from the University of Bath in the UK suggests a standard unit for measuring cannabis potency, similar to how we quantify alcohol consumption with standard drinks, could help people manage their intake and identify those at risk of cannabis use disorder, according to an article from ScienceAlert. As more countries introduce laws allowing for medicinal and recreational cannabis use, such standard measures could help inform public health strategies around harm reduction. For instance, a 0.45 gram joint of strong herbal cannabis might contain 12.78 standard THC units, while a weaker, seeded herbal cannabis can contain just 3.78 THC units, according to the new estimates. Researchers found that a common antibiotic-resistant bacterium prevents wounds from healing by chemically paralyzing skin cells rather than attacking them directly, according to an article from SciTechDaily. Scientists from an international research group led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), have identified an approach that may help chronic wounds heal faster, including wounds infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Chronic wounds are a serious global health burden. An estimated 18.6 million people develop diabetic foot ulcers each year worldwide, and as many as one in three people with diabetes may face a foot ulcer at some point in their lives. These long-lasting wounds are a major driver of lower limb amputations. They also often become trapped in a cycle of ongoing infection that keeps the body from repairing the damaged skin.  Age-verification is all the rage these days. Governments around the world are putting pressure on tech companies to make sure users are actually the age they should be in order to access their services, according to an article from Lifehacker. Sometimes, that means uploading an ID to prove your age; other times, it involves an AI system guessing how old you are based on your appearance, activity, and behavior. Roblox is the latest platform to roll out new age-verification rules, following intense criticism from parents, researchers, and even attorneys general, who, among other claims, assert that Roblox enables predators to connect with children via the platform. In response, the company announced new age-verification rules last September and November before rolling them out in select countries in December. This week, Roblox put them into effect in the U.S. That all sounds good—the problem is, the system is a bit of a disaster. From the “whoa boy … this really sounds like a great idea” department [/sarcasm], OpenAI announced its new ChatGPT Health feature, which will let users upload their medical records and ask health related questions, according to an article from Lifehacker. However, it might not be the best idea for you to do it, for both reliability and privacy reasons. The new ChatGPT Health feature will be a sandboxed tab inside the app that is isolated from your conversation history in other conversations with the chatbot. This tab also allows users to connect a variety of health-tracking apps like Apple Health, MyFitnessPal, and Peloton, as well as uploading medical records directly. (You won’t find me signing up to surrender my privacy any time soon!) Scientists have devised the most detailed map to date of the terrain hidden below the vast ice sheet blanketing Antarctica, uncovering an exuberant landscape of mountains, canyons, valleys and plains while discerning for the first time tens of thousands of hills and other smaller features, according to an article from Reuters. The researchers used the latest high-resolution satellite observations and a method called ice-flow perturbation analysis, which estimates subglacial topography and conditions based on surface features, to map the full continent including previously uncharted parts. Improved knowledge of the subglacial bedrock landscape may aid in forecasts concerning the climate-related retreat of Antarctica's ice sheet. Previous research indicated that rough terrain like jagged hillsides and mountaintops can slow this retreat.  Are you tired of all the bloatware on your new Android phone? Any new phone almost certainly comes with a handful of preinstalled apps you'll never use, regardless of which manufacturer you buy from or which operating system you're on, according to an article from Lifehacker. Some devices are more bloated than others: Google Pixels have a relatively “clean” build compared to Samsung phones, for example, and don't typically come with third-party apps and games. But you may still want to eliminate apps and features that clutter your home screen, take up valuable space, and create a drag on performance, especially if you have alternatives you like more. On Android, that likely means uninstalling what you easily can and disabling everything else. Ibuprofen’s anti-inflammatory action may influence cancer risk, but evidence remains complex and routine use for prevention is not advised, according to an article from SciTechDaily. Ibuprofen is one of the most widely used pain relievers, commonly taken for headaches, menstrual pain, and other everyday aches. New research suggests that its effects may extend beyond pain relief and could include potential anti-cancer benefits. As scientists continue to explore how chronic inflammation contributes to cancer, ibuprofen has drawn growing attention. This has prompted fresh discussion about whether a familiar over-the-counter drug might also play a role in reducing cancer risk. Food delivery platform Grubhub has confirmed a recent data breach after hackers accessed its systems, with sources telling BleepingComputer the company is now facing extortion demands, according to an exclusive story from BleepingComputer. Grubhub would not respond to any further questions regarding the breach, including when it occurred, whether customer data was involved, or if they were being extorted. While Grubhub would not share further details, multiple sources have told BleepingComputer that the ShinyHunters cybercrime group is extorting the company. According to sources, the threat actors are demanding a Bitcoin payment to prevent the release of older Salesforce data from a February 2025 breach and newer Zendesk data that was stolen in the recent breach.  Image by b0red from Pixabay Bacteria and the viruses that infect them, called phages, are locked in an evolutionary arms race. But that evolution follows a different trajectory when the battle takes place in microgravity, a study conducted aboard the International Space Station (ISS) reveals, according to an article from LiveScience. As bacteria and phages duke it out, bacteria evolve better defenses to survive while phages evolve new ways to penetrate those defenses. The new study, published Jan. 13 in the journal PLOS Biology, details how that skirmish unfolds in space and reveals insights that could help us design better drugs for antibiotic-resistant bacteria on Earth. In the study, researchers compared populations of E. coli infected with a phage known as T7. One set of microbes was incubated aboard the ISS, while identical control groups were grown on Earth. For the first time, researchers at the University of British Columbia have shown how to consistently produce a crucial type of human immune cell, known as helper T cells, from stem cells in a controlled lab setting, according to an article from Science Daily. The research, published on January 7 in Cell Stem Cell, removes a major barrier that has slowed the development, affordability, and large-scale production of cell therapies. By solving this problem, the work could help make off-the-shelf treatments more accessible and effective for conditions such as cancer, infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and more. The evolution of display technology has long chased a moving target: how to achieve full flexibility without sacrificing brightness or performance, according to an article from TechSpot. Now, a collaboration between Drexel University and Seoul National University has delivered a major advance, building a stretchable OLED that doubles in size while preserving a steady glow and record efficiency. The breakthrough is based on a class of materials known as MXenes: ultrathin, highly conductive sheets that combine the mechanical resilience of metals with the flexibility of polymers. Co-discovered by Drexel materials scientist Yury Gogotsi, MXenes are layered carbides and nitrides that can deform through bending and sliding between layers rather than fracturing. Researchers have now demonstrated that when used as the transparent electrode in OLEDs, MXenes outperform the industry's standard material, indium tin oxide (ITO), in both stretchability and brightness.  Image by Gordon Johnson from Pixabay Scientists at the University of New Mexico have uncovered an unexpected connection between the immune system and brain health, according to an article from ScienceDaily. Their research shows that OTULIN, an enzyme known for regulating immune activity, also plays a major role in producing tau, a protein closely tied to Alzheimer's disease, other neurodegenerative disorders, brain inflammation, and aging. The findings suggest that a single immune related protein may influence several processes involved in how the brain deteriorates over time. Despite its importance, the heart is one of the few tissues in the human body that can't repair damage very well – or at least, that's what has long been presumed, according to an article from ScienceAlert. Scientists in Australia have now caught heart muscle cells freely regenerating after a heart attack. When something impedes blood flow, the lack of oxygen kills heart cells. The organ can patch itself up with scar tissue, but this inelastic, fibrous tissue doesn't beat, making the heart less efficient. These irregularities can eventually lead to further attacks and heart failure in the future. Mice seem to be lucky enough to have hearts that can regenerate, at least partly. Their cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) have been seen dividing again after a heart attack, but human heart cells aren't nearly so sprightly after injury. Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions, according to an article from SciTechDaily. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called “triglycerides”, especially when those calories come from carbs, sugar, fats, and alcohol. Triglycerides are a type of fat or “lipid”, and the body stores them in fat cells to use as fuel between meals. However, too much of this fat can become harmful. High triglyceride levels can lead to “hypertriglyceridemia” (“excess triglycerides in the blood”), a condition tied to a much higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and pancreatitis. That is why people are widely encouraged to support healthy triglyceride levels through diet and exercise, while more severe cases may require medication. |








